PET
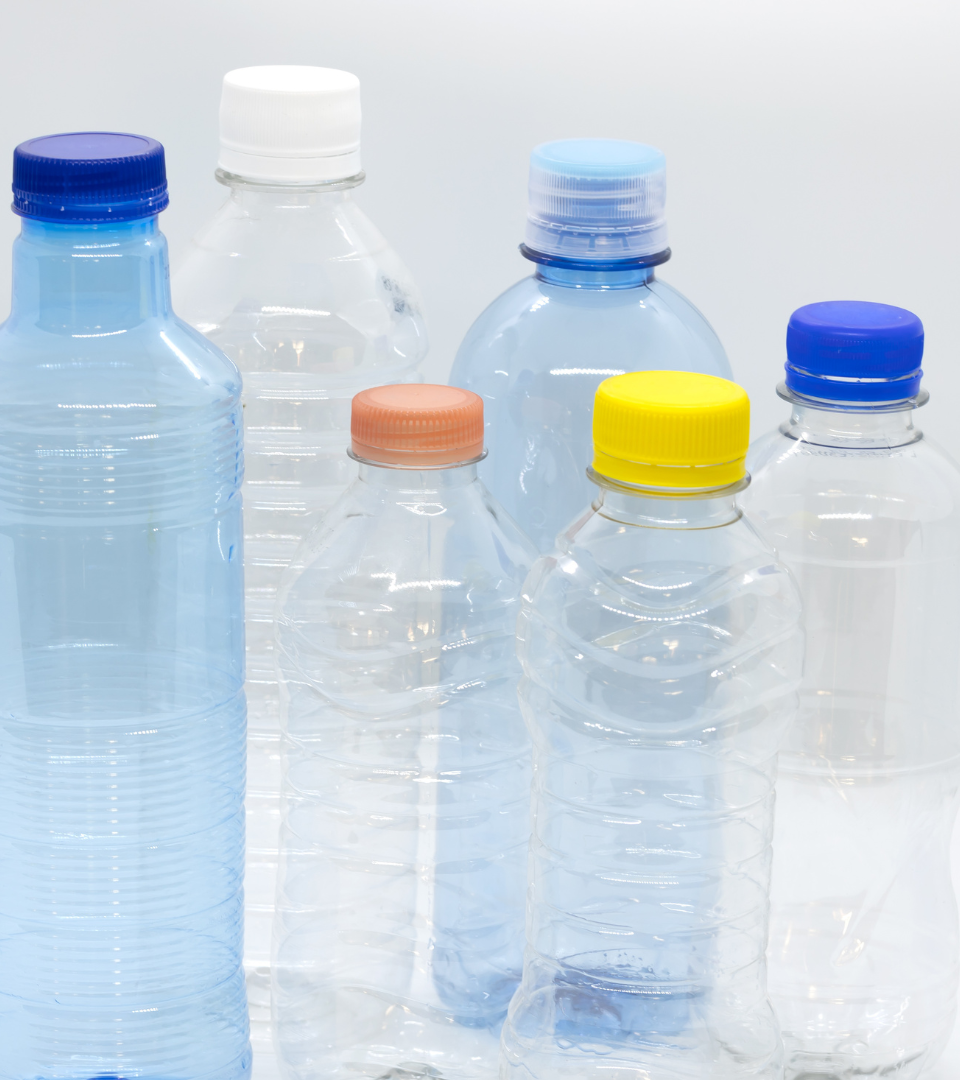
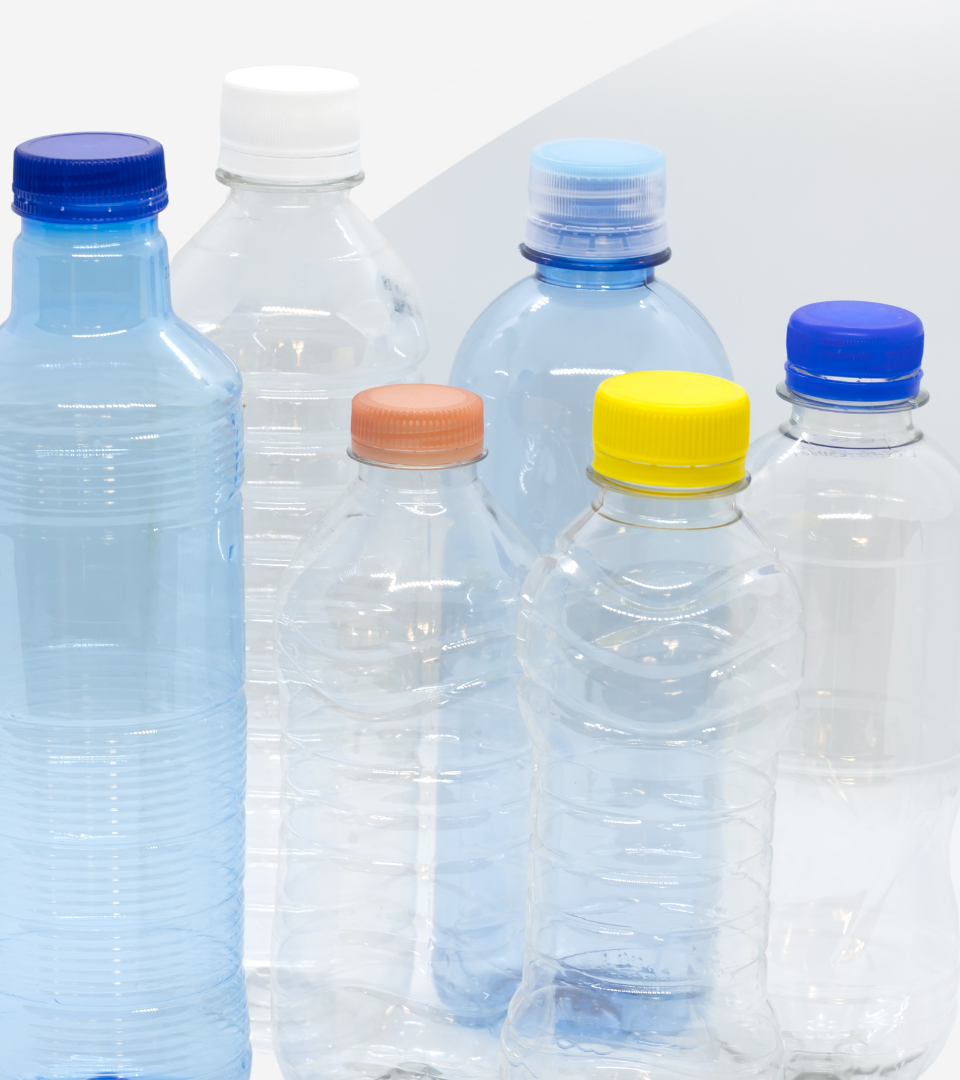
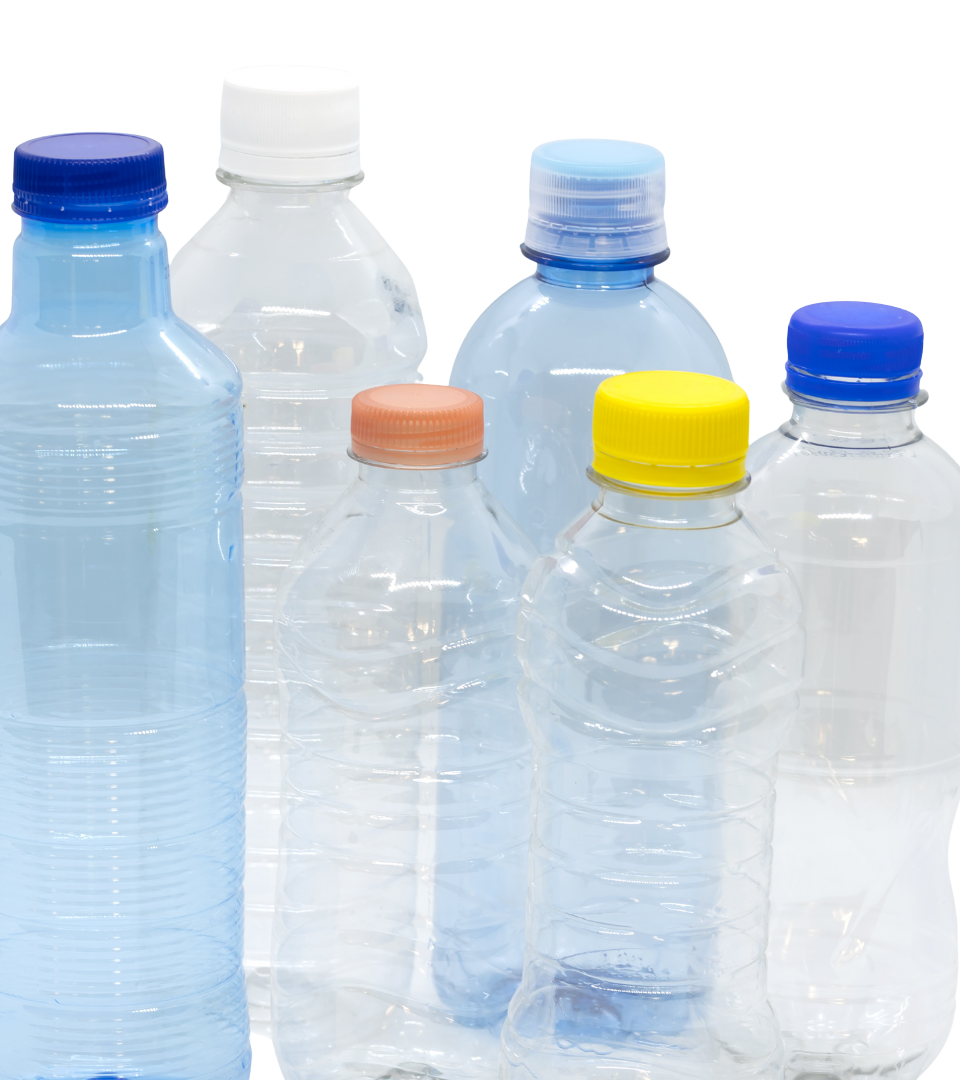





PET
PET is short for Polyethylene Terephthalate, which is the chemical name for Polyester.
PET is widely used for food and beverages packaging, fiber, fabric applications, and yarn-grade films for a wide range of applications.
Properties:
It offers the following advantages:
- Fully Recyclable: It is the most recyclable plastic globally. It is commercially recycled through re-melting, or chemical treatment.
- Sustainable: Its high strength-weight ratio accounts for its high energy efficiency where it
can pack more products compared to other packaging material, and hence uses less fuel for transport - Safe and hygienic: Health and safety agencies around the world approve PET as safe for contact
with food and beverages because of its non-reactive, non-toxic, and biologically-inert properties - Superior thermoplastic qualities: It is superior to other thermoplastic polymers in a number of aspects including tensile strength,
service-temperature range, electrical insulation; and gas, moisture, and chemical resistance - Polyester: PET is popularly known as polyester when used for fiber or fabric applications. It was originally synthesized
in North America in the 1940s as a fabric. Today, a majority of world’s synthetic fiber is made of polyester. - PET Resin: PET is the world’s preferred packaging material for food products, especially for carbonated soft drinks and mineral
water because of its non-toxic, non-reactive, and biologically-inert nature.
These qualities also make it a widely-used packaging material for personal care, medical, and pharmaceutical products.
PET treated with special additives is used for microwave food containers, trays, and packaging films. - PET Films: PET film is a biaxially-oriented form of polyester that is used as the most common substrate in the converting industry.
It is also widely used for food packaging, magnetic tapes, and functional films for
LCD displays because of its excellent tensile strength, heat resistance, and dimensional stability.